Hello all,
I’ve been scratching my head with a strange issue I am facing with brms.
I produced plots from a brms model under Windows using conditional_effects(). I migrated my project to Linux and ensured that dependencies were the same using renv. I used the same package and R versions (see attached files).
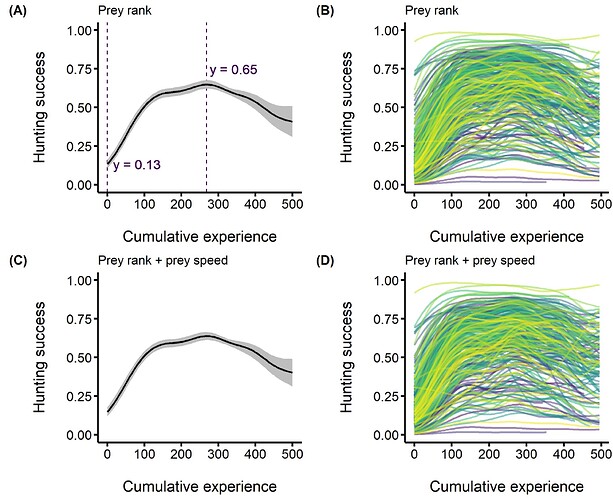
We can see the differences in this figure :
- The left part shows the predictions under Windows for two models
- The right part shows the predictions under Linux Pop OS for the same two models
I did not refit the models under the different operating systems, I just imported the .rds files and computed the predictions (see R code below).
I’d love to know why this occurs and how we can correct it. This is for an upcoming scientific publication and I want the process to be as reproducible as possible. Running the code in any OS should result in the same outputs since they are from the same model, no?
Please find attached two files in the thread so that people can go and try reproducing my problem.
- sessionInfo() under Windows
- sessionInfo() under Linux (Pop OS)
Here is a link to the model files to reproduce the results. You can download GAMM-II.rds and GAMM-V.rds : OSF | Model outputs from: Prey movement shapes the acquisition of predator expertise in a virtual bi-trophic system
Here is the link to the raw data : GitHub - quantitative-ecologist/predator-expertise: Data and code for Fraser Franco et al. XXXX
Here is the code to generate the plots.
# ==========================================================================
# Plot GAMM models
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
# 1. Prepare script
# ==========================================================================
# Load libraries and model -------------------------------------------------
options(mc.cores = parallel::detectCores())
library(parallel)
library(brms)
library(data.table)
library(ggplot2)
library(ggpubr)
library(viridis)
path <- file.path(getwd(), "outputs", "outputs_models")
mod1 <- readRDS(file.path(path, "GAMM-II.rds"))
mod2 <- readRDS(file.path(path, "GAMM-V.rds"))
# Load the data ------------------------------------------------------------
data <- fread(
"./data/FraserFrancoetal2023-data.csv",
select = c("predator_id",
"game_duration",
"pred_speed",
"prey_avg_speed",
"prey_avg_rank",
"cumul_xp_pred",
"total_xp_pred",
"hunting_success")
)
data[, predator_id := as.factor(predator_id)]
# Post processing preparations for custom family ---------------------------
expose_functions(mod1, vectorize = TRUE)
# Define the log likelihood function
log_lik_beta_binomial2 <- function(i, prep) {
mu <- brms::get_dpar(prep, "mu", i = i)
phi <- brms::get_dpar(prep, "phi", i = i)
trials <- prep$data$vint1[i]
y <- prep$data$Y[i]
beta_binomial2_lpmf(y, mu, phi, trials)
}
# Define function for posterior_predict
posterior_predict_beta_binomial2 <- function(i, prep, ...) {
mu <- brms::get_dpar(prep, "mu", i = i)
phi <- brms::get_dpar(prep, "phi", i = i)
trials <- prep$data$vint1[i]
beta_binomial2_rng(mu, phi, trials)
}
# Define function for posterior_epred
posterior_epred_beta_binomial2 <- function(prep) {
mu <- brms::get_dpar(prep, "mu")
trials <- prep$data$vint1
trials <- matrix(trials, nrow = nrow(mu), ncol = ncol(mu), byrow = TRUE)
mu * trials
}
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
# 2. Prepare the data for the plots
# ==========================================================================
# Prepare the plots --------------------------------------------------------
# Group-level smooths model 1
tab1_a <- conditional_effects(
mod1, method = "fitted",
effects = "Zcumul_xp:predator_id",
robust = TRUE, re_formula = NULL
)
tab1_a <- data.table(tab1_a[[1]])
# Cumulative XP global trend model 1
tab1_b <- conditional_effects(
mod1, method = "fitted",
robust = TRUE, re_formula = NULL,
effects = "Zcumul_xp",
conditions = data.frame(predator_id = NA)
)
tab1_b <- data.table(tab1_b[[1]])
# Group-level smooths model 2
tab2_a <- conditional_effects(
mod2, method = "fitted",
effects = "Zcumul_xp:predator_id",
robust = TRUE, re_formula = NULL
)
tab2_a <- data.table(tab2_a[[1]])
# Cumulative XP global trend model 2
tab2_b <- conditional_effects(
mod2, method = "fitted",
robust = TRUE, re_formula = NULL,
effects = "Zcumul_xp",
conditions = data.frame(predator_id = NA)
)
tab2_b <- data.table(tab2_b[[1]])
# Transform values --------------------------------------------------------
# Back transform x-axis values
sequence <- (seq(0, 500, 100) - mean(data$cumul_xp_pred))
standev <- sd(data$cumul_xp_pred)
scaled_breaks <- sequence / standev
# List the tables
tables <- list(
tab1_a, tab1_b,
tab2_a, tab2_b
)
names(tables) <- c(
"tab1_a", "tab1_b",
"tab2_a", "tab2_b"
)
# Function to apply transformation
# Computes non standardized cumulative XP
func <- function(x) {
x[, cumul_xp := (Zcumul_xp * standev) + mean(data$cumul_xp_pred)]
}
# Apply function
lapply(tables, func)
# Cut fitted values based on player XP ------------------------------------
# Extract player IDs with their total XP from the original data
xp <- unique(data[, .(predator_id, total_xp_pred)])
# Merge the two tables adding the total XP
tab1_a <- merge(tab1_a, xp, by = "predator_id")
tab2_a <- merge(tab2_a, xp, by = "predator_id")
# Cut all matches where fitted values are above total XP
tab1_a <- tab1_a[cumul_xp <= total_xp_pred, ]
tab2_a <- tab2_a[cumul_xp <= total_xp_pred, ]
# Setup a custom theme for the plot ----------------------------------------
custom_theme <- theme(
# axis values size
axis.text = element_text(face = "plain",
size = 14,
color = "black"),
# axis ticks lenght
axis.ticks.length = unit(.15, "cm"),
# axis ticks width
axis.ticks = element_line(linewidth = 0.90,
color = "black"),
# axis titles size
axis.title = element_text(size = 16,
face = "plain",
color = "black"),
axis.line = element_line(linewidth = 0.95,
color = "black"),
legend.position = "none",
panel.grid = element_blank(),
panel.background = element_blank()
)
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
# 3. Individual variance plots
# ==========================================================================
# Model 1 rank only --------------------------------------------------------
options(bitmapType = "cairo")
plot1_a <- ggplot(
tab1_a,
aes(x = Zcumul_xp,
y = estimate__ / 4,
color = predator_id)
) +
geom_line(linewidth = 1, alpha = 0.5) +
scale_color_viridis(discrete = TRUE, option = "D") + #B
ylab("Hunting success\n") +
ggtitle("Prey rank") +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = seq(0, 1, 0.25),
limits = c(0, 1)) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = scaled_breaks,
labels = seq(0, 500, 100)) +
xlab("\nCumulative experience") +
custom_theme
# Model 2 rank + speed -----------------------------------------------------
plot2_a <- ggplot(
tab2_a,
aes(x = Zcumul_xp,
y = estimate__ / 4,
color = predator_id)
) +
geom_line(linewidth = 1, alpha = 0.5) +
scale_color_viridis(discrete = TRUE, option = "D") + #B
ylab("Hunting success\n") +
ggtitle("Prey rank + prey speed") +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = seq(0, 1, 0.25),
limits = c(0, 1)) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = scaled_breaks,
labels = seq(0, 500, 100)) +
xlab("\nCumulative experience") +
custom_theme
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
# 4. Global trend plots
# ==========================================================================
# Model 1 rank only --------------------------------------------------------
plot1_b <- ggplot(
tab1_b,
aes(x = Zcumul_xp,
y = estimate__ / 4)
) +
geom_vline(
xintercept = min(tab1_b$Zcumul_xp),
lty = "dashed",
color = "#440154"
) +
geom_text(
aes(label = paste("y =", round(min(tab1_b$estimate__ / 4), digits = 2)),
y = min(tab1_b$estimate__ / 4),
x = min(tab1_b$Zcumul_xp) + 0.6),
color = "#440154",
size = 5
) +
geom_vline(
xintercept = tab1_b[which.max(estimate__), Zcumul_xp],
lty = "dashed",
color = "#440154"
) +
geom_text(
aes(label = paste("y =", format(round(max(tab1_b$estimate__ / 4), digits = 2), nsmall = 2)),
y = max(tab1_b$estimate__ / 4) + 0.10,
x = tab1_b[which.max(estimate__), Zcumul_xp] + 0.55),
color = "#440154",
size = 5
) +
geom_ribbon(
aes(
ymin = lower__ / 4,
ymax = upper__ / 4
),
fill = "gray"
) +
geom_line(linewidth = 1) +
ylab("Hunting success\n") +
ggtitle("Prey rank") +
scale_y_continuous(
breaks = seq(0, 1, 0.25),
limits = c(0, 1)
) +
scale_x_continuous(
breaks = scaled_breaks,
labels = seq(0, 500, 100)
) +
xlab("\nCumulative experience") +
custom_theme
# Model 2 rank + speed -----------------------------------------------------
# Predicted values from the GAMM
predicted_values <- tab2_b$estimate__
# Define the x-axis range
x <- tab2_b$Zcumul_xp
# Fit a spline to the predicted values
spline_fit <- splinefun(x, predicted_values)
# Calculate the first derivative using finite differences
dx <- mean(diff(x))
derivatives <- diff(predicted_values) / dx
# Establish the treshold at a value very close to 0 since its optimization
threshold <- 0.0088
# Find the point where the slope is close to zero
stabilized_point <- x[which(abs(derivatives) <= threshold)][1]
plot2_b <- ggplot(
tab2_b,
aes(x = Zcumul_xp,
y = estimate__ / 4)
) +
geom_vline(
xintercept = min(tab2_b$Zcumul_xp),
lty = "dashed",
color = "#440154"
) +
geom_text(
aes(label = paste("y =", round(min(tab2_b$estimate__ / 4), digits = 2)),
y = min(tab2_b$estimate__ / 4),
x = min(tab2_b$Zcumul_xp) + 0.6),
color = "#440154",
size = 5
) +
geom_vline(
xintercept = tab2_b[Zcumul_xp == stabilized_point]$Zcumul_xp,
lty = "dashed",
color = "#440154"
) +
geom_text(
aes(label = paste(
"y =",
format(
round(tab2_b[Zcumul_xp == stabilized_point]$estimate__ / 4, digits = 2),
nsmall = 2
)
),
y = (tab2_b[Zcumul_xp == stabilized_point]$estimate__ / 4) + 0.10,
x = tab2_b[Zcumul_xp == stabilized_point]$Zcumul_xp + 0.3),
color = "#440154",
size = 5
) +
geom_ribbon(
aes(
ymin = lower__ / 4,
ymax = upper__ / 4
),
fill = "gray"
) +
geom_line(linewidth = 1) +
ylab("Hunting success\n") +
ggtitle("Prey rank + prey speed") +
scale_y_continuous(
breaks = seq(0, 1, 0.25),
limits = c(0, 1)
) +
scale_x_continuous(
breaks = scaled_breaks,
labels = seq(0, 500, 100)
) +
xlab("\nCumulative experience") +
custom_theme
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
# 3. Combine plots into 1 figure
# ==========================================================================
# Prepare figure ------------------------------------------------------------
# Arrange paneled figure
figure <- ggarrange(
NULL, plot1_b, NULL, plot1_a,
NULL, plot2_b, NULL, plot2_a,
ncol = 4, nrow = 2,
labels = c(
"(A)", "", "(B)", "",
"(C)", "", "(D)", ""
),
widths = c(
0.15, 1.5, 0.15, 1.5,
0.15, 1.5, 0.15, 1.5
)
)
# Export the figure -----------------------------------------------------
path <- file.path(getwd(), "outputs", "outputs_figures")
ggexport(
figure,
filename = file.path(path, "figure1.png"),
width = 2700,
height = 2200,
res = 300
)
# ==========================================================================
# ==========================================================================
Thank you very much for your help!
I’m hopeful that the community will help me find answers.
Best
Maxime
session_infoLinux.txt (3.3 KB)
session_infoWindows.txt (2.8 KB)